|
Primorsk, Leningrad Oblast
Primorsk (; ; ) is a coastal town in Vyborgsky District of Leningrad Oblast, Russia and is the second largest Russian port on the Baltic, after St. Petersburg. It is located on the Karelian Isthmus, west of St. Petersburg, at the northern coast of the Gulf of Finland, near Beryozovye Islands (; ) which are protected as a sea bird sanctuary. Population: History It was first mentioned in Russian chronicles as Beryozovskoye (, lit. ''birch settlement'') in 1268, when the Hanseatic merchants from Gotland petitioned the Novgorod Republic to secure their passage to the Neva River. The original Finnish name Koivisto means "a group of birch trees", "a birch forest". Swedish name Björkö means "birch island". Swedes annexed the region during the Third Swedish Crusade. Novgorod formally ceded the area to Sweden in the Treaty of Nöteborg in 1323. Thereafter Primorsk was organized under the control of the Fief of Viborg. It became a separate parish from the parish of Viborg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
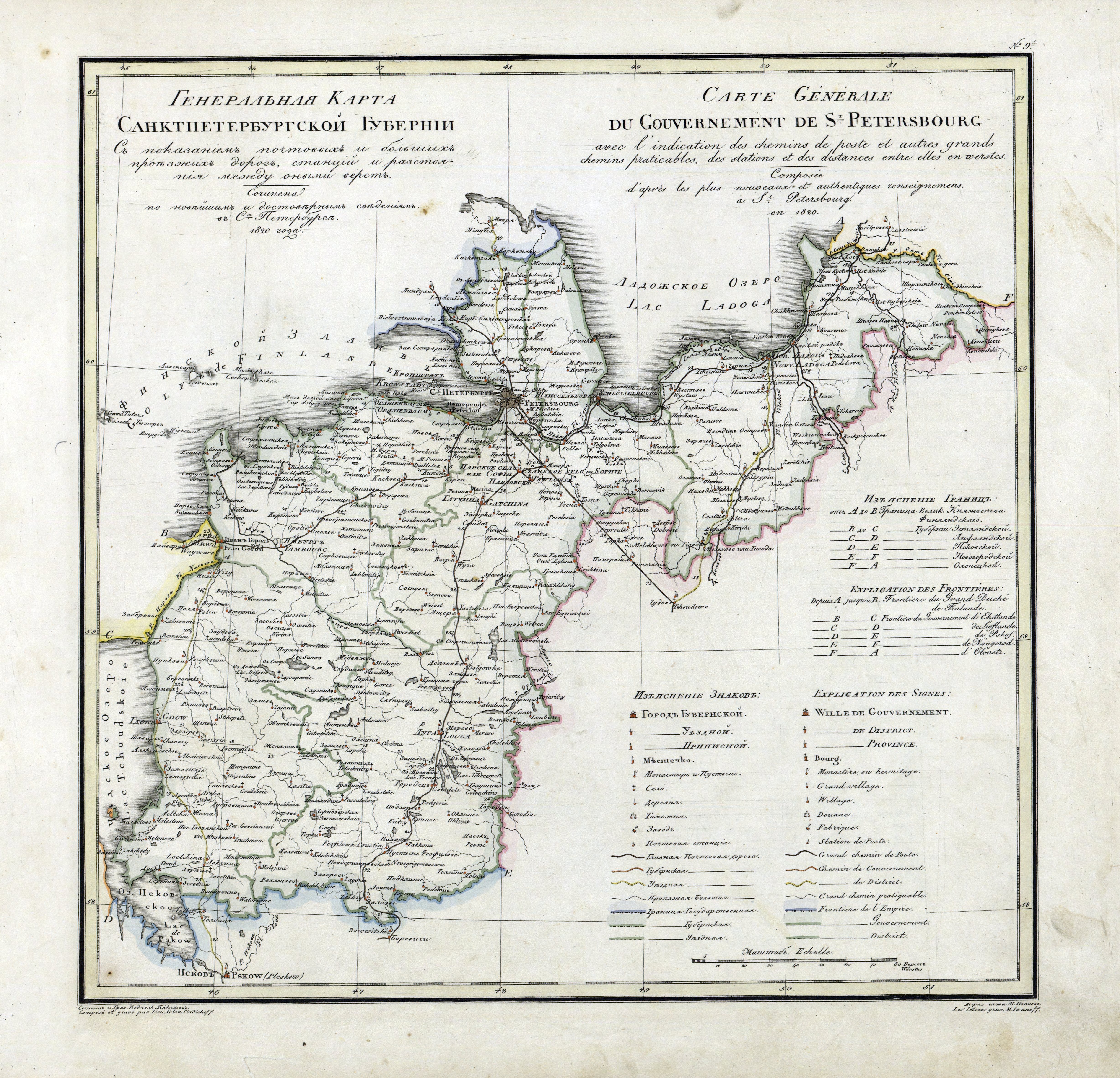
Leningrad Oblast
Leningrad Oblast (, ; ; ) is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast). The oblast has an area of and a population of 2,000,997 (2021 Russian census, 2021 Census); up from 1,716,868 recorded in the 2010 Russian census, 2010 Census. Leningrad Oblast is highly industrialized. Its administrative center and largest city is Gatchina. The oblast was established on 1 August 1927, although it was not until 1946 that the oblast's borders had been mostly settled in their present position. The oblast was named after the city of Saint Petersburg, Leningrad. In 1991, the city restored its original name, Saint Petersburg, but the oblast retains the name of Leningrad. It overlaps the historical region of Ingria, and is bordered by Finland (Kymenlaakso and South Karelia) in the northwest and Estonia (Ida-Viru County) in the west, as well as five federal subjects of Russia: the Republic of Karelia in the northeast, Vologda Oblast in the east, Novgorod Oblast in the sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Swedish Crusade
The Third Swedish Crusade to Finland was a Swedish military expedition against the pagan Karelia (historical province of Finland), Karelians from 1293 to 1295 in which the Swedes successfully expanded their borders eastwards and gained further control of their lands in Finland. After the crusade, Western Karelia remained under Swedish rule until the Treaty of Nystad in 1721. Background It followed the possibly mythical First Swedish Crusade, First Crusade and the Second Swedish Crusade, Second Crusade to Finland. Viborg Castle was established in 1293 on the site of a destroyed Karelian fort as the easternmost outpost of the medieval Kingdom of Sweden. The name of the expedition is largely anachronistic, and it was a part of the Northern Crusades. According to ''Erik's Chronicle'' (''Erikskrönikan'') the reason behind the expedition was pagan intrusions into Christian territories. According to ''Erik's Chronicle'', the Swedes conquered 14 Hundred (county division), hundreds from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viipuri Province
Viipuri Province was a Historical provinces of Finland, historical province of Finland from 1812 to 1945. History The predecessor of the province was Vyborg Governorate, which was established in 1744 from territories ceded by the Swedish Empire to Russia in 1721 (Treaty of Nystad) and in 1743 (Treaty of Åbo). These territories originated as parts of the Viborg and Nyslott County and Kexholm County in 1721, and parts of the Savolax and Kymmenegård County in 1743. The governorate was also known as Old Finland. During the Napoleonic Wars, the Kingdom of Sweden (1721–1809), Kingdom of Sweden had allied itself with the Russian Empire, United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom and other parties against First French Empire, Napoleonic France. However, following the Treaties of Tilsit, Treaty of Tilsit in 1807, Russia made peace with France. In 1808, supported by France, Russia successfully challenged Swedish control over Finland in the Finnish War. In the Treaty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vyborg
Vyborg (; , ; , ; , ) is a town and the administrative center of Vyborgsky District in Leningrad Oblast, Russia. It lies on the Karelian Isthmus near the head of Vyborg Bay, northwest of St. Petersburg, east of the Finnish capital Helsinki, and south of Russia's border with Finland, where the Saimaa Canal enters the Gulf of Finland. The most recent census population of Vyborg is Vyborg was founded as a medieval fortress in Finland under Swedish rule during the Third Swedish Crusade. After numerous wars between the Russians and Swedes, the Treaty of Nöteborg in 1323 defined the border of eastern Finland, and would separate the two cultures. Vyborg remained under Swedish rule until it was captured by the Russians during the Great Northern War. Under Russian rule, Vyborg was the seat of Vyborg Governorate until it was incorporated into the newly established Grand Duchy of Finland, an autonomous part of the Russian Empire. Finland declared its independence from R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vyborg Governorate
Vyborg Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (''guberniya'') of the Russian Empire. It was established in 1744 in newly ceded territories from Swedish Empire, Sweden following the Treaty of Åbo and parts of Saint Petersburg Governorate which were previously ceded by Sweden in 1721 as a result of the Great Northern War. In the Treaty of Nystad of 1721, Sweden formally ceded control of parts of the Viborg and Nyslott County and the Kexholm County located on the Karelian Isthmus and Lake Ladoga region to Russia. First these areas were part of the Saint Petersburg Governorate. Vyborg Governorate was established in 1744 when Sweden ceded control of parts of Kymmenegård and Nyslott County (which had been parts of Viborg and Nyslott County prior to the Treaty of Nystad) by the Treaty of Åbo. In Sweden (including Finland), the area of the governorate was also known as Old Finland (, ), and between 1802 and 1812 it was named the "Finland Governorate". Initially the gove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Finland
Old Finland (; ; ) is a name used for the areas that Russia gained from Sweden in the Great Northern War (1700–1721) and the Russo-Swedish War (1741–1743), and which were united as the Vyborg Governorate in 1744. During the Finnish War of 1808–1809, Russia annexed the rest of the present-day Finland, and formed the autonomous Grand Duchy of Finland ("New Finland") out of those areas. Old Finland was joined to the Grand Duchy in 1812 as Viipuri Province. History In the Treaty of Nystad (1721) that concluded the Great Northern War, Sweden was forced to cede Käkisalmi County and Viborg/Viipuri County to Russia. The ceded Finnish-speaking Ingria around Saint Petersburg, however, was not included in Old Finland. In the Treaty of Åbo (1743) Sweden had to cede the areas in southern Karelia east of the Kymi river and around Savonlinna to Russia. The Russian ruler guaranteed religion, property rights, old Swedish laws, and some privileges to the inhabitants of these terr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Petersburg Governorate
Saint Petersburg Governorate was a province (''guberniya'') of the Russian Empire, with its capital in Saint Petersburg. The governorate was composed of of area and 2,112,033 inhabitants. It was bordered by Governorate of Estonia, Estonian and Governorate of Livonia, Livonian Governorates to the west, Pskov Governorate to the south, Novgorod Governorate to the east, Olonets Governorate to the northeast, and Viipuri Province, Vyborg Governorate of the Grand Duchy of Finland to the north. The governorate covered most of the areas of modern Leningrad Oblast and Ida-Viru County, Ida-Viru, Jõgeva County, Jõgeva, Tartu County, Tartu, Põlva County, Põlva, and Võru County, Võru counties of Estonia. Establishment Ingermanland Governorate (, ''Ingermanlandskaya guberniya'') was created from the territories reconquered from the Swedish Empire in the Great Northern War. In 1704 prince Alexander Menshikov was appointed as its first governor, and in 1706 it was first Russian region des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vyborg Province, Saint Petersburg Governorate
Vyborg (; , ; , ; , ) is a town and the administrative center of Vyborgsky District in Leningrad Oblast, Russia. It lies on the Karelian Isthmus near the head of Vyborg Bay, northwest of St. Petersburg, east of the Finnish capital Helsinki, and south of Russia's border with Finland, where the Saimaa Canal enters the Gulf of Finland. The most recent census population of Vyborg is Vyborg was founded as a medieval fortress in Finland under Swedish rule during the Third Swedish Crusade. After numerous wars between the Russians and Swedes, the Treaty of Nöteborg in 1323 defined the border of eastern Finland, and would separate the two cultures. Vyborg remained under Swedish rule until it was captured by the Russians during the Great Northern War. Under Russian rule, Vyborg was the seat of Vyborg Governorate until it was incorporated into the newly established Grand Duchy of Finland, an autonomous part of the Russian Empire. Finland declared its independence from Russia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Administrative Divisions Of Russia In 1719–1725
Major events The second administrative reform of 1719 was carried out by Peter the Great in order to fix the deficiencies of the original system. On June 9 (May 29 in the Julian calendar), 1719 Peter issued an ukase (edict) that abolished the division of the governorates into ''lots'' (). Instead, most of the Governorates were divided into ''provinces'' (провинции), and provinces were further subdivided into ''districts'' (дистрикты). Provinces were governed by '' voyevodas''. The idea of the subdivision of governorates into province was borrowed from the administrative division system of Sweden and other European countries. Districts were introduced to replace the old system of subdivision into ''uyezds''; however, the borders of the new districts did not match those of the old ''uyezds''. The purpose of the districts was also different from that of the ''uyezds''—population of each district was taxed to support military units assigned to it. *June 9 (May 29 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter The Great
Peter I (, ; – ), better known as Peter the Great, was the Sovereign, Tsar and Grand Prince of all Russia, Tsar of all Russia from 1682 and the first Emperor of Russia, Emperor of all Russia from 1721 until his death in 1725. He reigned jointly with his half-brother Ivan V of Russia, Ivan V until 1696. From this year, Peter was an Absolute monarchy, absolute monarch, an autocrat who remained the ultimate authority and organized a well-ordered police state. Much of Peter's reign was consumed by lengthy wars against the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman and Swedish Empire, Swedish empires. His Azov campaigns were followed by the foundation of the Imperial Russian Navy, Russian Navy; after his victory in the Great Northern War, Russia annexed a Treaty of Nystad, significant portion of the eastern Baltic Sea, Baltic coastline and was officially renamed from a Tsardom of Russia, tsardom to an Russian Empire, empire. Peter led a cultural revolution that replaced some of the traditionalist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsar
Tsar (; also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar''; ; ; sr-Cyrl-Latn, цар, car) is a title historically used by Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word '' caesar'', which was intended to mean ''emperor'' in the European medieval sense of the term—a ruler with the same rank as a Roman emperor, holding it by the approval of another emperor or a supreme ecclesiastical official—but was usually considered by Western Europeans to be equivalent to "king". Tsar and its variants were the official titles in the First Bulgarian Empire (681–1018), Second Bulgarian Empire (1185–1396), the Kingdom of Bulgaria (1908–1946), the Serbian Empire (1346–1371), and the Tsardom of Russia (1547–1721). The first ruler to adopt the title ''tsar'' was Simeon I of Bulgaria. Simeon II, the last tsar of Bulgaria, is the last person to have held this title. Meaning in Slavic languages The title tsar is derived from the Latin title for the Roman emperors, ''c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Nystad
The Treaty of Nystad, or the Treaty of Uusikaupunki, was the last peace treaty of the Great Northern War of 1700–1721. It was concluded between the Tsardom of Russia and the Swedish Empire on in the then Swedish town of Nystad (, in the south-west of present-day Finland). Sweden had settled with the other parties in Stockholm (1719 and 1720) and in Frederiksborg (1720). During the war Peter I of Russia had occupied all Swedish possessions on the eastern Baltic coast: Swedish Ingria (where he began to build the soon-to-be Russian capital of St. Petersburg in 1703), Swedish Estonia and Swedish Livonia (which had capitulated in 1710), and Finland. In Nystad, King Frederick I of Sweden formally recognized the transfer of Estonia, Livonia, Ingria, and Southeast Finland ( Kexholms län and part of Karelian Isthmus) to Russia in exchange for two million silver thaler, while Russia returned the bulk of Finland to Swedish rule. The Treaty enshrined the rights of the Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |